Firmware 파일시스템 변조
TP-Link AX1500 공유기 내의 세부 동작을 분석하기 위해서 라우터 내부 쉘에 접근이 접근이 가능한지 확인해보려고 합니다.
먼저 Router Shell을 얻기 위한 방법을 4가지 정도 추려보았습니다.
- Firmware Update 페이지
- CFE Console
- UART를 통한 Shell 획득
- 1-day를 이용한 Shell 획득
해당 글은 1. Firmware Update 페이지를 통해 조작된 펌웨어를 업로드 하여 Shell을 얻기 위한 시도를 한 것이며, 이 과정에서 얻은 정보나 펌웨어를 조작하는 방법에 대해 다룹니다.
Firmware
TP-Link AX1500에 대한 펌웨어를 얻기 위해서 아래의 링크를 펌웨어를 다운 받습나다.
https://www.tp-link.com/us/support/download/archer-ax1500/v1.20/#Firmware
2024-01-30 - latest
펌웨어 확인
binwalk를 통해 해당 펌웨어의 구조를 파악하면 아래와 같이 Squashfs 라는 파일 시스템이 존재합니다.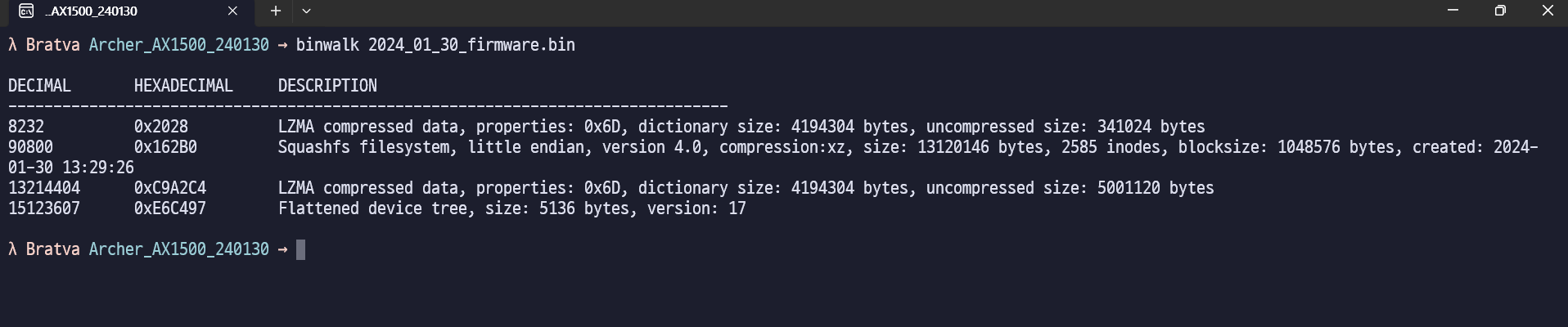
squashfs 카빙
dd명령어를 이용해 squashfs가 존재하는 부분을 카빙합니다.1 2 3 4
dd if=2024_01_30_firmware.bin skip=90800 bs=1 of=carving_firm 15081414+0 records in 15081414+0 records out 15081414 bytes (15 MB, 14 MiB) copied, 26.2231 s, 575 kB/s
unsquashfs
unsquashfs를 이용해 카빙한 데이터를 풀면 다음과 같이 여러 디렉토리가 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.1
unsquashfs carving_firm
FDT (Flattend Device Tree)
binwalk로 firmware를 보다가 fdt라는 부분이 있어서 이 부분을 뜯어보았습니다.
FDT는 하드웨어의 구조를 기술하기 위한 데이터 구조이며, 운영체제에게 타겟이 되는 전체 하드웨어를 구성하는 각 디바이스들의 구조 및 구성 방식을 전달하기 위해 사용됩니다.
- https://linuxfactory.or.kr/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=fdt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
$ binwalk carving_firm
DECIMAL HEXADECIMAL DESCRIPTION
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0x0 Squashfs filesystem, little endian, version 4.0, compression:xz, size: 13120146 bytes, 2585 inodes, blocksize: 1048576 bytes, created: 2024-01-30 13:29:26
13123604 0xC84014 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x6D, dictionary size: 4194304 bytes, uncompressed size: 5001120 bytes
15032807 0xE561E7 Flattened device tree, size: 5136 bytes, version: 17
Squashfs를 카빙한 것처럼 FDT가 존재하는 부분을 카빙합니다.
1 2 3 4
$ dd if=carving_firm skip=15032807 bs=1 of=fdt.dtb 48607+0 records in 48607+0 records out 48607 bytes (49 kB, 47 KiB) copied, 0.0487078 s, 998 kB/s
dtc command 설치
1
sudo apt install device-tree-compiler
dtb to dts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
$ dtc -s -I dtb fdt.dtb -O dts -o fdt.dts fdt.dts: Warning (reg_format): /ubus@ff800000/gpio-controller@0xff800504:reg: property has invalid length (20 bytes) (#address-cells == 1, #size-cells == 1) fdt.dts: Warning (unit_address_vs_reg): /memory: node has a reg or ranges property, but no unit name fdt.dts: Warning (unit_address_vs_reg): /clocks/i2s_clkmclk_syscon: node has a reg or ranges property, but no unit name fdt.dts: Warning (unit_address_vs_reg): /ubus@ff800000/bcm63xx-i2s: node has a reg or ranges property, but no unit name fdt.dts: Warning (pci_device_reg): Failed prerequisite 'reg_format' fdt.dts: Warning (pci_device_bus_num): Failed prerequisite 'reg_format' fdt.dts: Warning (simple_bus_reg): Failed prerequisite 'reg_format' fdt.dts: Warning (i2c_bus_reg): Failed prerequisite 'reg_format' fdt.dts: Warning (spi_bus_reg): Failed prerequisite 'reg_format'
결과 FDT 데이터를 문자열 데이터로 뽑아내면 다음과 같이 하드웨어의 정보들을 볼 수 있습니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284
/dts-v1/; /memreserve/ 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000008000; /memreserve/ 0x0000000004000000 0x0000000000100000; / { #address-cells = <0x01>; #size-cells = <0x01>; compatible = "brcm,bcm963178"; interrupt-parent = <0x01>; model = "Broadcom BCM963178"; brcm-legacy { compatible = "brcm,brcm-legacy"; }; brcm-therm { compatible = "brcm,therm"; status = "okay"; }; chosen { bootargs = "console=ttyAMA0 init=/etc/preinit earlyprintk debug irqaffinity=0 pci=pcie_bus_safe"; }; clocks { #address-cells = <0x01>; #size-cells = <0x01>; ranges; i2s_clkmclk_syscon { compatible = "brcm,i2s-audio-clkmclk-syscon\0syscon"; linux,phandle = <0x06>; phandle = <0x06>; reg = <0xff802080 0x04>; }; i2sclk { #clock-cells = <0x00>; clk-mclk-syscon = <0x06>; clock-output-names = "i2s_clk"; clocks = <0x05>; compatible = "brcm,i2s-clock"; linux,phandle = <0x07>; phandle = <0x07>; }; oscillator { #clock-cells = <0x00>; clock-frequency = <0xbebc200>; compatible = "fixed-clock"; linux,phandle = <0x05>; phandle = <0x05>; }; }; cpus { #address-cells = <0x01>; #size-cells = <0x00>; cpu@0 { compatible = "arm,cortex-a7"; device_type = "cpu"; linux,phandle = <0x03>; next-level-cache = <0x02>; phandle = <0x03>; reg = <0x00>; }; cpu@1 { compatible = "arm,cortex-a7"; device_type = "cpu"; enable-method = "brcm,bca-smp"; linux,phandle = <0x04>; next-level-cache = <0x02>; phandle = <0x04>; reg = <0x01>; }; cpu@2 { compatible = "arm,cortex-a7"; device_type = "cpu"; enable-method = "brcm,bca-smp"; next-level-cache = <0x02>; reg = <0x02>; }; l2-cache0 { compatible = "cache"; linux,phandle = <0x02>; phandle = <0x02>; }; }; cs4345 { compatible = "crus,cs4345-dac"; }; interrupt-controller@81000000 { #address-cells = <0x00>; #interrupt-cells = <0x03>; compatible = "arm,cortex-a7-gic"; interrupt-controller; linux,phandle = <0x01>; phandle = <0x01>; reg = <0x81001000 0x1000 0x81002000 0x2000>; }; memory { device_type = "memory"; reg = <0x00 0x4000000>; }; pcie@80040000 { #address-cells = <0x03>; #interrupt-cells = <0x01>; #size-cells = <0x02>; brcm,coreid = <0x00>; compatible = "brcm,bcm963xx-pcie"; device_type = "pci"; interrupt-map = <0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x2b 0x04>; interrupt-map-mask = <0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00>; interrupt-names = "intr"; interrupts = <0x00 0x2b 0x04>; ranges = <0x2000000 0x00 0xc0000000 0xc0000000 0x00 0x10000000>; reg = <0x80040000 0xa000>; }; pcie@84000000 { brcm,coreid = <0x01>; compatible = "brcm,bcm963xx-vpcie"; device_type = "vpci"; reg = <0x84000000 0x1000000>; }; pmu { compatible = "arm,cortex-a7-pmu"; interrupt-affinity = <0x03 0x04>; interrupts = <0x00 0x07 0x04 0x00 0x08 0x04>; }; reserved-memory { #address-cells = <0x01>; #size-cells = <0x01>; ranges; }; rng@ff800b80 { compatible = "brcm,iproc-rng200"; reg = <0xff800b80 0x28>; }; timer { arm,cpu-registers-not-fw-configured = <0x01>; compatible = "arm,armv7-timer"; interrupts = <0x01 0x0d 0x308 0x01 0x0e 0x308 0x01 0x0b 0x308 0x01 0x0a 0x308>; }; uartclk { #clock-cells = <0x00>; clock-frequency = <0x2faf080>; compatible = "fixed-clock"; linux,phandle = <0x08>; phandle = <0x08>; }; ubus@ff800000 { #address-cells = <0x01>; #size-cells = <0x01>; compatible = "simple-bus"; ranges = <0x00 0xff800000 0x7fffff>; bcm63xx-i2s { clock-names = "i2sclk\0i2sosc"; clocks = <0x07 0x05>; compatible = "brcm,bcm63xx-i2s"; interrupts = <0x00 0x4e 0x04>; reg = <0x2080 0x21>; }; gpio-controller@0xff800500 { #gpio-cells = <0x02>; compatible = "brcm,bcm6345-gpio"; gpio-controller; ngpios = <0x20>; reg = <0x500 0x04 0x520 0x04>; reg-names = "dirout\0dat"; }; gpio-controller@0xff800504 { #gpio-cells = <0x02>; compatible = "brcm,bcm6345-gpio"; gpio-controller; ngpios = <0x20>; reg = <0x504 0x04 0x00 0x524 0x04>; reg-names = "dirout\0dat"; }; gpio-controller@0xff800508 { #gpio-cells = <0x02>; compatible = "brcm,bcm6345-gpio"; gpio-controller; ngpios = <0x20>; reg = <0x508 0x04 0x528 0x04>; reg-names = "dirout\0dat"; }; gpio-controller@0xff80050c { #gpio-cells = <0x02>; compatible = "brcm,bcm6345-gpio"; gpio-controller; ngpios = <0x20>; reg = <0x50c 0x04 0x52c 0x04>; reg-names = "dirout\0dat"; }; gpio-controller@0xff800510 { #gpio-cells = <0x02>; compatible = "brcm,bcm6345-gpio"; gpio-controller; ngpios = <0x20>; reg = <0x510 0x04 0x530 0x04>; reg-names = "dirout\0dat"; }; gpio-controller@0xff800514 { #gpio-cells = <0x02>; compatible = "brcm,bcm6345-gpio"; gpio-controller; ngpios = <0x20>; reg = <0x514 0x04 0x534 0x04>; reg-names = "dirout\0dat"; }; gpio-controller@0xff800518 { #gpio-cells = <0x02>; compatible = "brcm,bcm6345-gpio"; gpio-controller; ngpios = <0x20>; reg = <0x518 0x04 0x538 0x04>; reg-names = "dirout\0dat"; }; gpio-controller@0xff80051c { #gpio-cells = <0x02>; compatible = "brcm,bcm6345-gpio"; gpio-controller; ngpios = <0x20>; reg = <0x51c 0x04 0x53c 0x04>; reg-names = "dirout\0dat"; }; nand@ff801800 { #address-cells = <0x01>; #size-cells = <0x00>; compatible = "brcm,nand-bcm63xx\0brcm,brcmnand-v7.1"; reg = <0x1800 0x600 0x2000 0x10>; reg-names = "nand\0nand-int-base"; status = "okay"; nandcs@0 { compatible = "brcm,nandcs"; nand-on-flash-bbt; reg = <0x00>; }; }; serial@ff812000 { #address-cells = <0x01>; #size-cells = <0x01>; clock-names = "uartclk\0apb_pclk"; clocks = <0x08 0x08>; compatible = "arm,pl011\0arm,primecell"; interrupts = <0x00 0x20 0x04>; reg = <0x12000 0x1000>; }; watchdog@480 { compatible = "brcm,bcm96xxx-wdt"; reg = <0x480 0x10>; timeout-sec = <0x50>; }; }; };
결과를 보면 TP-Link AX1500에서 사용하는 cpu 정보나 chipset 모델 등의 정보를 볼 수 있었습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
#address-cells = <0x01>;
#size-cells = <0x01>;
compatible = "brcm,bcm963178";
interrupt-parent = <0x01>;
model = "Broadcom BCM963178";
brcm-legacy {
compatible = "brcm,brcm-legacy";
};
...
cpus {
#address-cells = <0x01>;
#size-cells = <0x00>;
cpu@0 {
compatible = "arm,cortex-a7";
device_type = "cpu";
linux,phandle = <0x03>;
next-level-cache = <0x02>;
phandle = <0x03>;
reg = <0x00>;
};
펌웨어 조작
펌웨어 내부의 쉘에 접속하기 위해서 telnet 데몬을 구동시켜 원격으로 접속하는 식으로 펌웨어를 변조하려고 합니다.
/etc/init.d/rcS 파일에 다음과 같이 telnet 데몬을 실행하는 코드 추가
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
config_load system
config_foreach system_config system
if [ "$1" = "S" -a "$foreground" != "1" ]; then
run_scripts "$1" "$2" &
elif [ "$1" = "K" ]; then
run_scripts_K "$1" "$2"
else
run_scripts "$1" "$2"
fi
/usr/sbin/telnetd -l /bin/sh
코드 추가 후 다시 파일시스템을 만들어 줍니다.
- 기존 squashfs가 block size가 1M 였으므로 고려하여 옵션 사용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
$ sudo mksquashfs squashfs-root squashfs_telnetd -comp xz -b 1M
Parallel mksquashfs: Using 16 processors
Creating 4.0 filesystem on squashfs_telnetd, block size 1048576.
[=========================================================================================================-] 1958/1958 100%
Exportable Squashfs 4.0 filesystem, xz compressed, data block size 1048576
compressed data, compressed metadata, compressed fragments,
compressed xattrs, compressed ids
duplicates are removed
Filesystem size 12809.41 Kbytes (12.51 Mbytes)
28.66% of uncompressed filesystem size (44700.89 Kbytes)
Inode table size 20126 bytes (19.65 Kbytes)
23.67% of uncompressed inode table size (85035 bytes)
Directory table size 23874 bytes (23.31 Kbytes)
46.83% of uncompressed directory table size (50982 bytes)
Number of duplicate files found 117
Number of inodes 2585
Number of files 1982
Number of fragments 41
Number of symbolic links 300
Number of device nodes 0
Number of fifo nodes 0
Number of socket nodes 0
Number of directories 303
Number of ids (unique uids + gids) 1
Number of uids 1
root (0)
Number of gids 1
root (0)
Result
결론을 말하자면 해당 방법으로 쉘을 획득할 수 는 없었습니다. 펌웨어 업데이트 페이지에서 펌웨어에 대한 검증을 시도하는 부분이 있어(CRC 등) 해당 부분을 우회하는 작업이 필요할 것 같았고, 해당 작업 시에 시간이 오래 걸릴 것 같아 해당 방법은 보류하기로 했습니다.